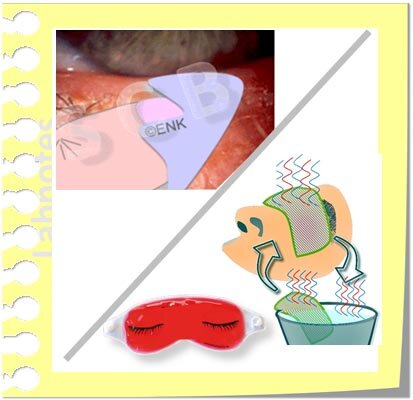
Steps in the staggered therapy for Dry Eye
=> here is more information, if necessary, on Severity Grades, Staggered-Therapy und some Background information
Mild dry eye
=> … get more information for a therapy option by a ´Click´ on an image
Mild dry eye
Definition : typically mild irritation of the eye without significant bothering and impairment of the daily routine
(occasionally more severe symptoms can contrast to mild clinical signs)
Clinical Signs :
a single sign is typically not sufficient for a reliable diagnosis of dry eye disease, but the overall clinical picture is crucial. An exception to this is the vital staining, as this directly indicates damage that has occurred.
surface damage/ vital staining: Oxford 1/5 (mild or absent staining)
reduction of tear film stability: FBUT ≤ 10 secs (typ. slightly reduced, but may be normal)
reduction of tear meniscus hight: TMH < 0,2 mm (slightly reduced)
aqueous secretion Schirmer-1 test: ≥ 10 mm/ 5 min (often normal)
or distinctly increased >> 20-25mm (in case of episodic stress lacrimation)
Therapy : patient information + avoidance of risk factors + eyelid therapy: basic
if there is a co-existing morbidity that can negatively affect a dry eye condition this should also be treated, e.g. internal risk factors such as chronic systemic diseases, or any disease condition at the ocular surface, such as e.g. overgrowth of demodex hair mites.
low-viscosity tear substitutes (approx. 5 times a day / every 2 hours) preferably with oil addition or additional liposomal spray
Moderately advanced dry eye
=> … get more information for a therapy option by a ´Click´ on an image
Moderate Dry Eye
Definition : significant bothering irritation of the eye with occasional impairment of the daily routine
(occasionally no symptoms reported or even severe symptoms with only moderate clinical signs)
Clinical Signs :
a single sign is typically not sufficient for a reliable diagnosis of dry eye disease, but the overall clinical picture is crucial. An exception to this is the vital staining, as this directly indicates damage that has occurred.
surface damage/ vital staining: Oxford 2/5 (in at least one eye, distinctly increased)
reduction of tear film stability: FBUT 4 secs - 9 secs (distinctly reduced)
reduction of tear meniscus hight: TMH < 0,1 mm (distinctly reduced)
aqueous secretion Schirmer-1 test: 4 mm - 9 mm (typ. distinctly reduced)
or distinctly increased >> 20-25 mm (in case of episodic stress lacrimation)
Therapy : patient information + avoidance of risk factors + lid therapy: basic
PLUS : low-viscosity tear substitutes => increase application up to every hour at most, preferably with additional increased functions e.g. for longer time of action, preferably with oil addition or additional liposomal spray
when application every hour is not sufficient, typically other therapy options are necessary - see below
PLUS : high viscosity gel or ointment at night
PLUS: prescription medicine from the eye doctor can be helpful in case of e.g. distinct inflammatory reactions, severe obstructive MGD with inspissated secretum or chronic blepharitis, particularly in combination with skin rosacea
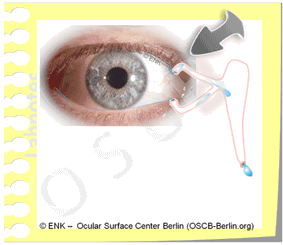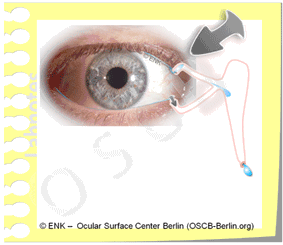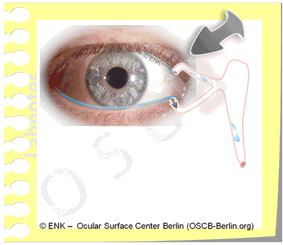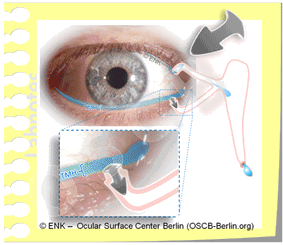
PLUS : In case of a dominating severe strong lack of tear volume, a temporary occlusion of the tear drainage into the nose, e.g. with ´Punctum Plugs´ can hold the own tears on the ocular surface and can reduce the frequency of tear supplement application.
PLUS : if necessary eyelid therapy with specialized apparative equipment in the eye doctor´s practise:
e.g. automated warming and squeezing (lipiflow) of the meibomian glands in the eyelids and / or
e.g Intense light therapy (intense pulsed light, IPL) or other types of light therapy such as color light therapy
Severe dry eye
=> … get more information for a therapy option by a ´Click´ on an image
Severe Dry Eye
Definition : severe bothering irritation the eye with constant impairment of the daily routine
Clinical Signs : severe pathologic test results
a single sign is typically not sufficient for a reliable diagnosis of dry eye disease, but the overall clinical picture is crucial. An exception to this is the vital staining, as this directly indicates damage that has occurred.
surface damage/ vital staining: Oxford 3/5 (in both eyes, strong staining)
reduction of tear film stability: FBUT 0 secs - 3 secs (severe reduction)
reduction of tear meniscus hight TMH 0 mm (severe reduction)
aqueous secretion Schirmer-1 test: 0 mm - 3 mm (severe reduction)
Therapy : patient information + avoidance of risk factors + lid therapy: basic
PLUS: high-viscosity Gel or Ointment also during day time, preferably with additional increased functions e.g. for longer time of action, preferably with oil addition or additional liposomal spray
PLUS: prescription medicine from the eye doctor
PLUS: temporary occlusion of the tear drainage into the nose, e.g. with ´Punctum Plugs´ can hold the own tears on the ocular surface and can reduce the frequency of tear supplement application.
PLUS: fitting of Scleral Contact Lenses can be helpful therapy option - if the patient is determined (!) to give this innovative therapy option a try
PLUS: Recommendation for referral to a specialized (university) Sicca Center
Very severe Dry Eye
The very severe dry eye is only marginally covered here, as it is a disease that belongs in intense clinical care, preferably in a university dry eye center. It will be decided there about the grade of severity and the appropriate therapy.
Characteristics
A very severe dry eye typically has a very severe lack of tears and severe tissue disorders. The lack of tears is often caused by a disorder of the lacrimal gland. The tissue damage can be caused by an underlying inflammatory disease, such as ocular mucosal pemphigoid, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) in the case of condition after bone marrow transplantation etc..
The wetting disorder leads to greatly increased friction on the ocular surface with severe tissue damage. In case of tear deficiency, there is a severe lack of active ingredients of the tears, which are important for keeping the ocular surface healthy. While 'lubrication' can be partially compensated by tear supplements, the lack of important active tear ingredients is difficult to compensate for.
When the surface destruction in Dry Eyes is to severe, that the visual function is endangered, own (autologous) serum eye drops may be recommended.
Tissue damage
In very severe dry eye, the disorder extends beyond the epithelial layer of the ocular surface. Disorders of the epithelium are responsible for the vital staining, the extent of which determines the degree of severity (from mild to moderate to severe) according to the Oxford Scheme. Epithelial damage can heal completely due to the constant normal formation of new epithelial cells.
Damage that goes beyond this, more precisely through the boundary layer of the epithelial basement membrane, and damages the connective tissue, typically leaves more or less pronounced scars. These cloud the transparency of the cornea and can thus cause more or less conspicuous visual disturbances.
In the very severe dry eye, changes typically occur that can cause permanent damage or may require invasive surgical treatment.
Typical damages are e.g:
Image of a very severe dry eye that shows corneal opacities, ingrowth of blood vessels, beginning conjunctivalization, in addition there is a chronic blepharitis.
Substance defects with subsequent sars and/ or with irregularities of the normally smooth regular surface
corneal opacities
damage of the corneal stem cells that are located at the corneal margin (limbus)
immigration of (opake) conjunctival tissue over the cornea, termed as conjunctivalization
and potentially many more
Typical therapy strategies
If there is an underlying inflammatory or other kind od disease, its treatment is in the foreground.
In addition, a symptomatic treatment with tear supplements and, if necessary, a supportive eyelid therapy are also important.
Above all, it is important that the surface of the eye is consistently cared for by sufficient tear substitutes - as with all degrees of dry eye disease.
In addition, if necessary, hygiene and care of the eyelids can be useful and, if necessary, a physical lid edge therapy.
Other therapy options are more invasive, e.g. :
Intensification of anti-inflammatory medication
chronic dry eye typically involves an inflammatory response that acts as a major amplifying mechanism of the disease, anti-inflammation is thus an important recent therapeutic principle
=> here is more information
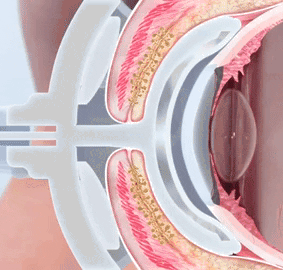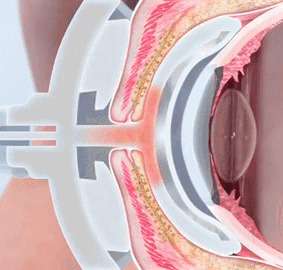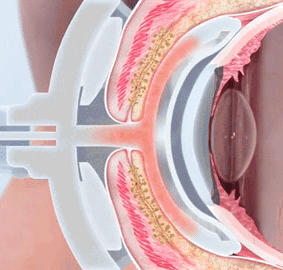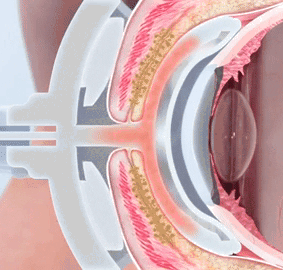
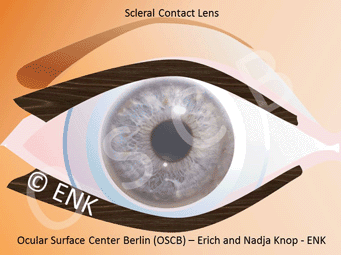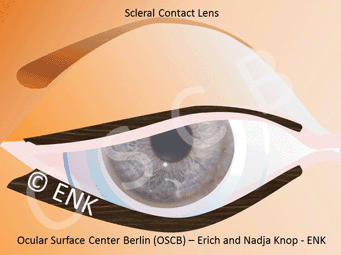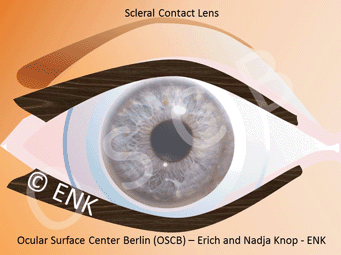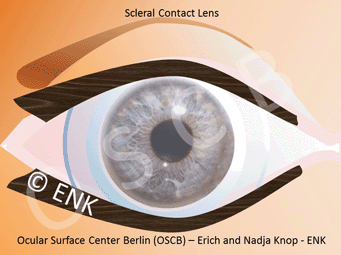
Scleral protective contact lenses
Scleral protective contact lenses are a special large type of contact lenses that vault the cornea and store a lake of moisture underneath the vault. Thus, they shield the surface of the eye from mechanical stimuli (e.g. friction during blinking) and keep the eye permanently moist and well. Such contact lenses can also promote improved self-healing of the altered tissue within this moist chamber. Scleral contact lenses are an often underappreciated treatment option.
=> here is more information
Autologous serum eye drops therapy
Blood is most certainly a very special juice ... it contains many important active substances for protection, nutrition, growth and regulation of tissues, as well as for other important functions. Since essential active ingredients of tear fluid come from blood, or at least have similarity with it, blood serum is practically also an ideal eye drop for tissue the disorders in severe dry eye.
Proprietary serum eye drops are derived from the serum of a patient's own blood - that’s why the are termed ´autologous´. Typically, about half a liter of blood is drawn and then autologous serum eye drops are made from the blood serum. For elderly, chronically ill and frail patients, it is sometimes not possible to draw such a quantity of blood on a regular basis. The amount is sufficient for about half a year of eye drop therapy, depending on the frequency of use and possible dilution. The drops are frozen in small vials and must after thawing be stored in the refrigerator, where they can only be used for a short time.
The production and dispensing of blood products such as serum eye drops are strictly regulated in most countries. This is because they contain not only many important active ingredients but also provide some dangers. Blood and blood products can contain dangerous pathogens and thus be infectious, they have antigenic properties that preclude their use in other people. Serum eye drops also represent an ideal nutrient medium for many bacteria, which is why they can easily germinate and spoil - their use is then a danger to the eye. They must therefore typically be prescribed by a doctor, manufactured by a blood bank and dispensed by a pharmacy. For more information please ask your eye doctor.
Autologous serum eye drops are typically prescribed only for very severe dry eye, when the tissue of the ocular surface is already so severely disturbed that it can no longer maintain itself, even with the help of common therapeutics as shown above, when the visual function of the eye is endangered, and when other therapeutic options, such as e.g. scleral protective contact lenses, are out of the question for various reasons.
Occasionally there is a certain 'hype' about autologous serum eye drops as a seemingly simple and quick solution for dry eyes. However, they are not just 'better tear substitutes' if you are not quite satisfied with commercially available preparations. Proprietary autologous serum eye drops are already an invasive therapeutic procedure that requires regular blood sampling and careful storage, through constant freezing to prevent infection. They are typically indicated only when the visual function of the eye is at risk, as a last therapeutic option before surgical therapy may be recommended.
If necessary, surgical therapy procedures are typically recommended (such as e.g. amniotic membrane suturing, stem cell transplantation etc.) may then be indicated to preserve the eye and vision.
Staggered Therapy
Dry eye diseas is a complex, chronic disorder and requires a similar therapy; this is typically a staggered step-by-step therapy according the severity grade of the patient:
It starts with informing the patient about his or her disease and ways to avoid the most important risk factors.
Then follows a basic therapy of the eyelids (physical eyelid therapy, hygiene and eyelid care) and with tear substitutes.
As the severity of the disease increases, further therapy steps are added.
Therapy Steps for:
Mild Dry Eyes
Moderat/ advanced Dry Eye Disease
Severe Dry Eye Disease
Stragegies for very severe Dry Eye Disease
Severity grade
With dry eyes, the strength of subjective complaints of the patient and the objective clinical findings do not always coincide, as studies show.
This is known as disparity of signs and symptoms which is probably due to the individually different processing by the nervous system with the pain system and higher emotional instances.
The mild dry eye typically occurs without significant impairment of the daily routine. However, even without significant clinical signs, or after the clinical signs have already improved a lot during the therapy, still a considerable subjective burden may occasionally be felt by a patient.
The ultimate evidence of clinical severity is determined by the degree of ocular surface damage, as identified by vital staining.
However, the severity of dry eye can also be described in a simplified and usually relatively reliable way by the degree of the patient's impairment:
Mild: typically mild irritation of the eye without significant bothering and impairment of the daily routine
Moderately advanced: significant bothering irritation of the eye with occasional impairment of the daily routine
Severey: severe bothering irritation of the eye with constant impairment of the daily routine
=> if necessary, here is some more Background Information about the therapy of dry eye disease.
Background Information
Dry eye disease is a complex disorder of the functional systems and structure of the ocular surface and it is negatively influenced by numerous risk factors. The pathology is based on the mutual negative influence of a tear film disorder and surface damage.
A deficiency of the tear film occurs typically first and is mostly due to a primary lack of oil on the tear film, whereas a primary lack of aqueous secretion is rare - in the further course of the disease both forms typically mix.
A disturbance of the pain system may lead to the development of a chronic pain syndrome that can become an independent disease factor.
An effective therapy of dry eye disease is based on a thorough investigation and diagnosis in order to find out which disease factors are most relevant for an individual patient.
Effective therapy options can then be applied in a staggered approach with progressive addition of therapy steps as described on the present page. Any individual therapy option is typically not effectve but a combined therapy that also addresses risk factors is advisable. It is important to note that, as the disease condition is chronic only a similarly chronic therapy can eventually be successful.
Luckily, intense research over the past decades has provided several novel therapy approaches such as e.g, physical therapy of Meibomian dysfunction (MGD). either as a basic therapy at home or by novel apparative equipment in the doctor´s practise. Furthermore, a specific anti-inflammatory therapy can provide great benefit for patients with chronic dry eye disease.
Although the therapy for dry eye disease is relatively advance nowadays, even the staggered therapy cannot be applied in a ´cooking book fashion´ but must always be adapted to the individual patient and his/ her disease and needs.